In the modern world, where chronic diseases, metabolic disorders, and lifestyle-induced ailments continue to rise, women face unique health challenges that require nuanced nutritional strategies. One increasingly popular and scientifically supported approach to optimal health is the Whole Food Plant-Based (WFPB) lifestyle. Integrating wfpb recipes into a woman’s daily regimen not only enhances nutrient density but also reduces the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. At the intersection of personalized nutrition and sustainable wellness, WFPB eating provides a holistic, effective, and compassionate foundation for long-term health. This article delves deeply into the essential dietary guidelines for women, emphasizing the transformative power of whole food plant-based diets and offering practical advice for real-world application.
You may also like: Top Expert-Recommended Vegan Main Meals to Fuel Women’s Health and Energy
Understanding Women’s Nutritional Needs Through the Lifecycle
Women’s nutritional requirements fluctuate significantly over the course of their lives. Puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, breastfeeding, menopause, and postmenopause all influence nutrient demands. Iron, calcium, vitamin D, folate, and omega-3 fatty acids become particularly critical during these transitional phases. Iron is essential due to menstrual blood loss, while calcium and vitamin D help maintain bone density, especially as women age and estrogen levels decline. Folate is crucial in childbearing years to prevent neural tube defects, and omega-3 fatty acids play a vital role in brain health and hormonal balance.
However, mainstream diets often fail to meet these needs without resorting to synthetic supplementation or animal-derived sources. By contrast, whole food plant-based diet recipes naturally supply a wide array of micronutrients through diverse, unprocessed plant sources. Foods like lentils, leafy greens, fortified plant milks, chia seeds, and flaxseeds can adequately support these needs when consumed strategically. For example, pairing vitamin C-rich foods like bell peppers or citrus fruits with iron-rich legumes enhances iron absorption, demonstrating how thoughtful food combinations can yield superior nutritional outcomes for women.
The Science-Backed Benefits of a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet for Women
Mounting scientific literature supports the claim that women who adhere to a whole food plant-based diet experience numerous health benefits. A consistent intake of whole food meals rich in fiber, antioxidants, phytonutrients, and plant-based proteins has been shown to lower blood pressure, reduce LDL cholesterol, and support healthy weight management. These outcomes are especially relevant for women, who statistically face higher risks for autoimmune diseases, osteoporosis, and certain reproductive cancers.
Whole food vegetable based diet recipes, which focus on foods in their most natural and unrefined forms, optimize metabolic efficiency by providing slow-digesting complex carbohydrates, anti-inflammatory fats, and bioavailable minerals. These nutrients contribute to stable blood sugar levels, mood regulation, and hormonal balance—factors that are central to female health. Moreover, the naturally lower caloric density of whole food dinners makes them ideal for maintaining a healthy weight without restrictive dieting, which can disrupt hormonal equilibrium and reproductive function.
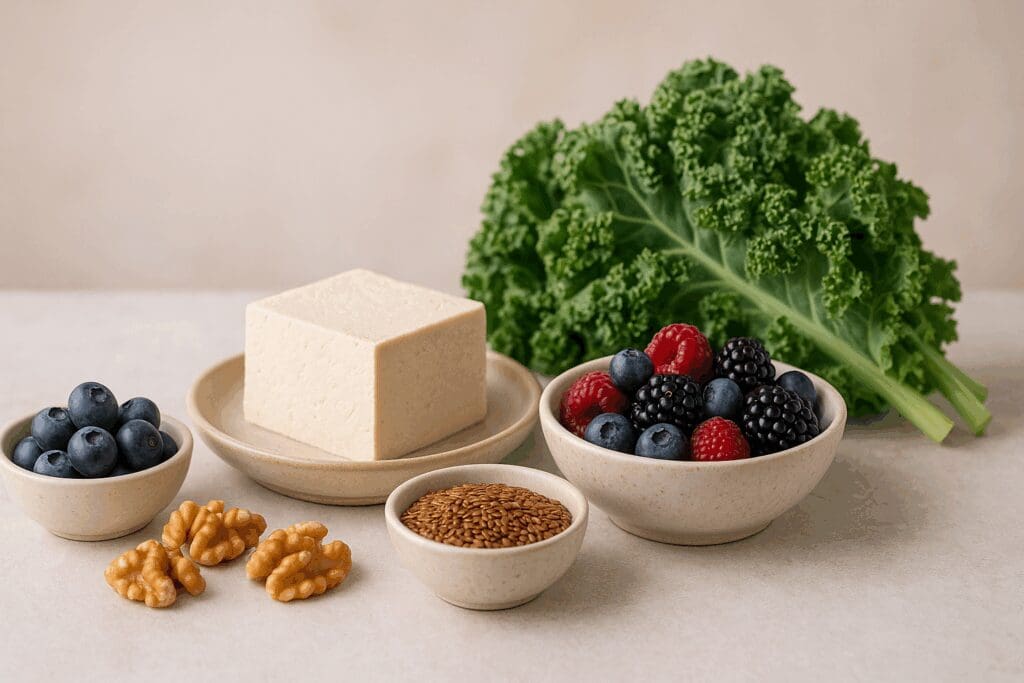

WFPB Recipes That Support Hormonal Harmony
Among the most compelling reasons for women to embrace wfpb recipes is their capacity to promote hormonal balance without the use of artificial interventions. Hormonal imbalances can manifest through irregular menstrual cycles, mood swings, skin issues, and weight gain. A whole food plant-based diet mitigates these symptoms by reducing intake of hormone-disrupting compounds commonly found in processed and animal-based foods.
Soy foods, such as tempeh, tofu, and edamame, contain phytoestrogens that can modulate estrogen activity in the body. Contrary to outdated misconceptions, research has found that these plant estrogens exert a balancing effect, especially during perimenopause and menopause, by attaching to estrogen receptors and either blocking or mimicking estrogen’s effects as needed. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale further support hormonal detoxification through compounds like indole-3-carbinol, which aids liver function and estrogen metabolism.
Moreover, easy unprocessed food recipes that include omega-3-rich ingredients such as chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds can significantly alleviate PMS symptoms and promote emotional well-being. When used consistently in whole food diet recipes, these ingredients cultivate a physiological environment conducive to hormonal stability.
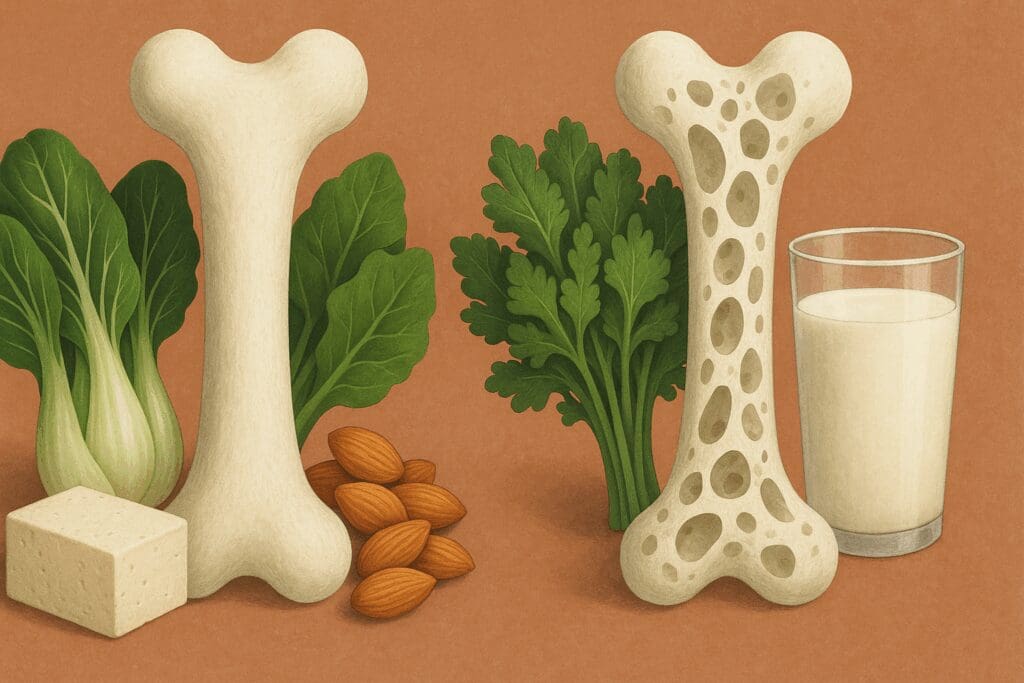

Powerful WFPB Recipes for Bone Health and Longevity
One of the greatest concerns among women, especially postmenopausal women, is bone health. Osteoporosis disproportionately affects women due to estrogen loss, which accelerates bone resorption. Traditional narratives have long emphasized dairy as the gold standard for calcium, yet a closer look reveals that calcium from leafy greens and fortified plant milks is not only bioavailable but also accompanied by other bone-supportive nutrients.
Incorporating wfpb recipes that include bok choy, collard greens, tahini, almonds, and calcium-set tofu can provide more than adequate calcium levels when consumed as part of a balanced diet. Vitamin K, essential for bone mineralization, is abundant in green vegetables, while magnesium from nuts and seeds ensures proper calcium utilization. Whole food recipes that combine these ingredients into delicious, satisfying meals ensure women are not only meeting their bone health needs but doing so in a way that aligns with overall disease prevention.
Further enhancing these benefits is the absence of high sodium levels and acidic protein breakdown products found in processed animal products, both of which have been linked to calcium leaching from bones. A lifetime of nutrient-dense whole food dinners rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents can thus serve as a foundation for longevity and skeletal resilience.
Whole Food Dinner Ideas for Reproductive Wellness
Reproductive health is often an overlooked yet foundational component of women’s well-being. From puberty through menopause, maintaining a fertile and balanced reproductive system is essential not just for childbearing, but for energy, vitality, and quality of life. Whole food plant based diet recipes rich in folate, zinc, vitamin B6, and omega-3s have been associated with improved fertility outcomes and better hormonal regulation.
For example, legumes like lentils and chickpeas, paired with whole grains such as quinoa or brown rice, form a complete protein profile that supports cell repair and hormone production. Berries, spinach, and sweet potatoes provide critical antioxidants that protect ovarian cells from oxidative stress. Easy unprocessed food recipes featuring these combinations not only taste vibrant but also work synergistically to optimize reproductive performance.
Moreover, whole food meals that limit trans fats and avoid refined sugars have been shown to positively influence menstrual regularity and decrease the severity of symptoms associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis. Nutritional choices that prioritize whole food dinners help create a hormonal ecosystem where balance, rather than disruption, becomes the norm.
Supporting Heart Health with Whole Food Recipes
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death among women globally. Despite this, many women are unaware that dietary interventions can dramatically reduce their risk profile. Whole food vegetable based diet recipes, when carefully crafted to include potassium-rich fruits, nitrate-dense leafy greens, and heart-healthy fats from avocados and seeds, can actively lower blood pressure and improve arterial flexibility.
Scientific studies have consistently found that diets high in fiber and low in saturated fat reduce the incidence of heart disease by regulating lipid profiles and preventing plaque buildup in arteries. Incorporating a wide array of colorful produce ensures a steady intake of flavonoids, polyphenols, and carotenoids—plant compounds known for their vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory properties.
Women who rely on whole food dinners rather than fast food or pre-packaged meals reduce their sodium intake significantly, thereby lowering the risk of hypertension. Moreover, consuming whole food plant based diet recipes that include legumes, oats, and barley can help regulate cholesterol levels. These foods naturally contain beta-glucans and other soluble fibers that bind to cholesterol in the digestive tract and facilitate its excretion.
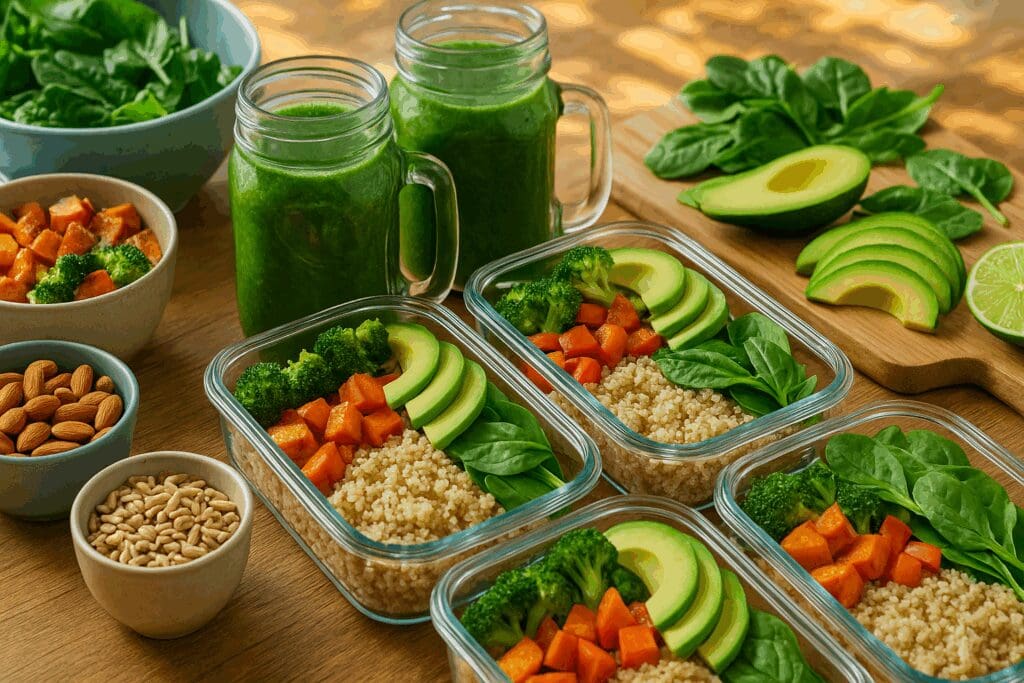

Easy Unprocessed Food Recipes for Everyday Energy
Daily energy levels can fluctuate widely based on hormonal cycles, stress, sleep, and diet. For women managing careers, families, and personal goals, maintaining consistent energy throughout the day is a necessity. Easy unprocessed food recipes built around whole food ingredients offer a sustainable energy source without the crashes associated with refined sugars or caffeinated stimulants.
Incorporating complex carbohydrates from sweet potatoes, quinoa, and legumes ensures a slow release of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing spikes and crashes. Adding healthy fats from avocados or flaxseed oil helps stabilize energy and improve cognitive function, while high-fiber vegetables like carrots and broccoli support gut health, which is intrinsically linked to mood and stamina.
Whole food meals that integrate adaptogenic herbs such as maca and ashwagandha, along with protein-rich plant sources like tempeh and lentils, provide a comprehensive energy solution for active women. These ingredients can be seamlessly included in hearty grain bowls, savory stews, or nutrient-packed smoothies—all staples in wfpb recipes that prioritize both flavor and function.
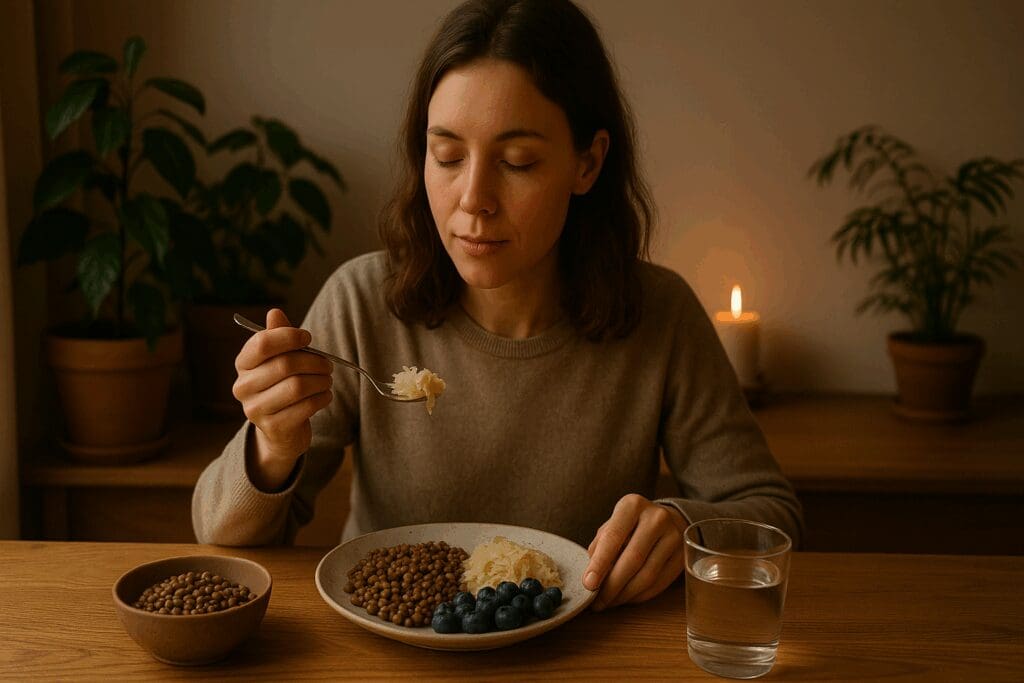

How Whole Food Dinners Enhance Mental Clarity and Mood
The gut-brain axis has emerged as a key area of focus in understanding mood disorders, cognitive function, and overall mental health. A growing body of evidence links dietary patterns to neurotransmitter activity, with gut flora playing a pivotal role in serotonin production. Whole food dinners rich in prebiotic fibers, fermented foods, and antioxidants enhance the diversity and resilience of the gut microbiome, creating a biochemical environment that fosters mental well-being.
Whole food diet recipes that include fermented vegetables, fiber-rich legumes, and polyphenol-laden fruits like blueberries and pomegranates contribute to improved mood stability and cognitive sharpness. These foods modulate inflammation, support blood-brain barrier integrity, and regulate cortisol levels, all of which are vital for maintaining mental clarity in high-stress environments.
Women who prioritize mental health through nutrition often report more consistent emotional regulation, improved sleep, and greater resilience against anxiety and depression. These benefits are particularly potent when dietary strategies are paired with lifestyle practices such as mindfulness, regular physical activity, and sleep hygiene.
Designing Sustainable Whole Food Meals for Long-Term Success
Adopting a whole food plant-based lifestyle is most effective when it is sustainable and enjoyable. Sustainability, in this context, involves not only environmental stewardship but also practical considerations like budget, time, and accessibility. Whole food meals can be designed to suit all of these constraints by focusing on batch cooking, seasonal produce, and pantry staples.
Planning whole food dinners in advance prevents reliance on processed convenience foods and allows for balanced nutrient distribution throughout the week. For instance, preparing a large pot of lentil stew or chickpea curry can provide several days’ worth of satisfying, nutrient-rich meals. Freezing portions and rotating dishes prevents mealtime fatigue and supports dietary adherence.
Seasonal ingredients often offer the most nutritional value at the lowest cost, making them a cornerstone of successful wfpb recipes. Root vegetables in winter, leafy greens in spring, berries in summer, and squash in autumn all bring unique flavors and benefits to the table. By developing culinary skills and exploring international cuisines, women can transform whole food dinners into a journey of discovery and empowerment.
Frequently Asked Questions: Nutritional Guidelines and Whole Food Living for Women
How can I transition to whole food dinners without feeling overwhelmed?
Transitioning to whole food dinners can feel intimidating at first, but the key is to begin with gradual, manageable changes. Start by swapping out one heavily processed meal per day for a simple dish made with whole food ingredients like brown rice, beans, and fresh vegetables. Batch cooking is a highly effective strategy to maintain consistency, especially for busy schedules. Focus on creating a short list of favorite whole food dinner ideas that you can rotate weekly to build familiarity. As your confidence grows, you can experiment with more complex whole food recipes and expand your grocery list to include seasonal and diverse plant-based ingredients.
What are the social challenges of following a whole food plant based diet, and how can I manage them?
Social situations, such as family gatherings or eating out, can present obstacles when you’re committed to a whole food plant based diet. One effective approach is to communicate your dietary needs with hosts or restaurants ahead of time, which often opens doors for accommodating options. Bringing your own easy unprocessed food recipes to potlucks can also normalize your choices and even inspire others. Developing a supportive community online or in-person can provide both emotional encouragement and new meal ideas. Over time, your friends and family may grow more accepting, especially as they witness your energy levels and overall well-being improve.
Are there specific whole food vegetable based diet recipes for athletic women?
Athletic women have unique nutritional demands, particularly regarding protein intake and muscle recovery. Whole food vegetable based diet recipes can easily meet these needs by incorporating high-protein plant sources such as lentils, quinoa, tempeh, and hemp seeds. Post-workout meals might include a chickpea and quinoa salad with tahini dressing or a smoothie made with almond butter, spinach, banana, and flaxseeds. For endurance athletes, complex carbohydrates from sweet potatoes, whole grains, and legumes provide sustained energy. These nutrient-dense options help enhance physical performance without relying on synthetic supplements or processed meal replacements.
How do easy unprocessed food recipes affect long-term gut health?
Easy unprocessed food recipes have a profound and lasting impact on gut health due to their high fiber and prebiotic content. These foods nourish beneficial gut bacteria, leading to improved digestion, immune function, and mental clarity. In contrast to ultra-processed meals, whole food recipes minimize exposure to preservatives, emulsifiers, and additives that can irritate the gut lining and disrupt the microbiome. Including a variety of fermented vegetables, legumes, and resistant starches creates an internal environment that supports microbial diversity. This microbial balance has been linked to a lower risk of conditions such as IBS, obesity, and even depression.
What makes wfpb recipes ideal for managing autoimmune conditions?
The anti-inflammatory nature of wfpb recipes makes them particularly well-suited for managing autoimmune conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. These recipes eliminate dairy, refined sugars, and processed oils—all of which can exacerbate inflammatory responses. Instead, they emphasize foods rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals, like berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables, which help modulate immune activity. Additionally, many whole food plant based diet recipes promote gut health, and since a significant portion of immune function is rooted in the gut, this offers an indirect yet powerful method of managing autoimmunity. Adopting this diet under medical supervision can complement other therapeutic interventions and potentially reduce medication dependency over time.
How can I make whole food diet recipes more affordable?
Contrary to popular belief, whole food diet recipes can be very budget-friendly when planned properly. Bulk staples such as dried beans, lentils, oats, and brown rice offer cost-effective sources of protein and energy. Shopping for seasonal produce not only saves money but also ensures that you are consuming fruits and vegetables at their peak nutritional value. Avoiding packaged snacks and ready-made meals offsets costs, as does cooking in batches and freezing portions for future use. Finally, using pantry staples creatively—like making vegetable broths from scraps or turning leftover grains into patties—helps reduce waste and maximize every dollar spent.
Can whole food meals support mental health beyond just nutrition?
Yes, whole food meals play a subtle but powerful role in supporting mental health beyond their nutrient profile. The act of preparing your own meals from scratch fosters mindfulness and provides a creative outlet, both of which are known to reduce stress and promote well-being. Establishing rituals around cooking and eating can create a sense of stability and purpose, which are psychologically grounding. Additionally, cultivating an intentional relationship with food often enhances self-efficacy and body awareness, counteracting disordered eating patterns. Over time, this holistic connection between food, body, and emotion can help reinforce healthier habits and improved self-esteem.
Are there cultural or global influences that shape whole food dinner ideas?
Whole food dinner ideas are often deeply rooted in traditional cuisines around the world, many of which naturally align with plant-based principles. For example, Mediterranean diets emphasize legumes, olive oil, and vegetables, while Ethiopian dishes use lentils, teff, and spiced stews. Indian cuisine offers a wide range of lentil-based dals, vegetable curries, and spice combinations that enhance both flavor and nutrition. Exploring these cultural influences can make transitioning to whole food dinners more exciting and less monotonous. In fact, many of the most nutrient-rich whole food recipes originate from cultures with lower incidences of chronic disease.
How do I deal with cravings for processed foods when following whole food recipes?
Managing cravings is an essential part of long-term success when following whole food recipes. One effective strategy is to identify the emotional triggers behind the craving—stress, boredom, or habit—and address them through alternative outlets such as physical activity, journaling, or meditation. Another technique is to recreate favorite processed snacks using whole food ingredients; for instance, you can make baked sweet potato chips with sea salt or a banana-oat cookie with dark chocolate. Ensuring that your meals are satisfying in flavor, texture, and portion size also prevents the feelings of deprivation that often fuel cravings. As your palate adjusts, you’ll likely find that the allure of highly processed foods diminishes naturally.
What role do wfpb recipes play in sustainable living?
Wfpb recipes are inherently aligned with sustainable living because they rely heavily on low-impact, minimally packaged, plant-based ingredients. Plant farming typically requires fewer natural resources like water and land compared to animal agriculture, and it produces significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing local, seasonal produce further reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation and storage. Additionally, minimizing food waste through meal planning and composting aligns with the sustainability ethos that underpins many whole food meals. By embracing a diet centered on whole food plant based diet recipes, individuals contribute to both personal health and planetary preservation.
Final Thoughts: Whole Food Nutrition as a Pathway to Empowered Well-Being
Incorporating whole food plant-based diet recipes into a woman’s nutritional strategy offers far-reaching benefits that extend beyond physical health. From hormonal harmony and reproductive vitality to mental clarity and cardiovascular protection, the impact of dietary choices is profound and multifaceted. When supported by easy unprocessed food recipes and thoughtfully curated whole food meals, this lifestyle becomes not a restriction but a revelation—a way to align body, mind, and values.
The growing availability of evidence-based guidance, combined with the accessibility of ingredients and cooking resources, makes now an ideal time to embark on this transformative journey. The power of nutrition lies not only in the prevention of disease but also in the cultivation of joy, resilience, and purpose. By embracing whole food vegetable based diet recipes and integrating them into daily routines, women can nourish themselves in ways that are both deeply personal and universally beneficial.
Ultimately, these dietary shifts offer more than just improved health metrics. They provide a foundation for self-respect, community engagement, and environmental responsibility. In this way, the choice to adopt wfpb recipes becomes a declaration of autonomy and a step toward a more compassionate and vibrant life.



