Understanding the Basics of Vaginal Fungal Infections
When it comes to addressing intimate health concerns, choosing the right treatment can be a delicate yet crucial decision. Among the most common issues affecting women of reproductive age is the vaginal yeast infection, a condition that often requires targeted intervention such as an anti fungal vaginal cream. These over-the-counter or prescription treatments are formulated to relieve itching, discharge, and irritation caused by an overgrowth of Candida species, typically Candida albicans, in the vaginal flora. Selecting the appropriate product depends not only on symptom severity but also on individual health history, sensitivities, and lifestyle.
Vaginal yeast infections are a form of vaginitis, representing one of the most common reasons women seek medical attention for genital symptoms. While these infections are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), sexual activity can sometimes disrupt the vaginal ecosystem, increasing the risk of developing an imbalance that favors fungal growth. Other contributing factors may include antibiotic use, hormonal changes, uncontrolled diabetes, or even prolonged use of tight, non-breathable clothing. Understanding the root causes of the infection is essential to choosing the most effective anti fungal vaginal cream tailored to one’s needs.
Women may encounter a wide variety of antifungal creams, each varying in strength, active ingredients, and delivery methods. Options range from single-day high-dose therapies to longer seven-day regimens that offer slower but steady relief. It’s not just about symptom suppression; the right antifungal cream can support the body’s natural defenses and restore a healthy pH balance when chosen wisely. Not all infections are created equal, and neither are the products designed to combat them.
To make an informed decision, women must understand the anatomy of a yeast infection, how antifungal medications work, and the indicators that suggest professional medical evaluation is necessary. Self-diagnosis may be effective for recurrent sufferers who recognize the signs, but misdiagnosis is common, especially when symptoms overlap with other vaginal or dermatological conditions like bacterial vaginosis, allergic reactions, or dermatophyte infections.
By exploring the mechanisms, formulations, and individual variations in susceptibility and response, this guide aims to demystify the process of selecting the best antifungal cream for private parts, specifically for the vaginal area. With a careful review of ingredients, safety profiles, and application techniques, readers will gain the confidence and clarity needed to navigate their treatment options with both autonomy and medical accuracy.
You may also like: The Essential Female Hygiene Checklist Every Woman Should Follow for Better Intimate Health
The Science Behind Vaginal Yeast Infections and Their Symptoms
A vaginal yeast infection, also known as vulvovaginal candidiasis, is a fungal overgrowth that can disrupt the natural microbiota of the vagina. In most cases, this overgrowth is due to Candida albicans, a yeast-like fungus that normally lives in the vaginal tract in harmless concentrations. However, under certain conditions, such as hormonal fluctuations, weakened immunity, antibiotic use, or high blood sugar levels, Candida can multiply rapidly and trigger an infection.
Clinically, the symptoms of a yeast infection can range from mild to severe. Common signs include persistent itching around the vulva and vaginal opening, thick and odorless white discharge often described as resembling cottage cheese, redness and swelling of the labia, and a burning sensation during urination or intercourse. These symptoms, while often distinct, can overlap with those of other vaginal conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis. It’s worth noting that not all women experience all symptoms, and some may suffer from only one or two that are particularly bothersome.
From a physiological perspective, the balance of Lactobacillus bacteria in the vagina plays a crucial role in maintaining an acidic pH, which in turn inhibits fungal growth. When this balance is disrupted, Candida has an opportunity to thrive. This explains why antibiotic use, which kills both harmful and beneficial bacteria, is a major risk factor for yeast infections. Similarly, elevated estrogen levels—whether from pregnancy, hormone therapy, or contraceptives—can also promote Candida colonization.
The inflammatory response mounted by the immune system against Candida is what causes many of the uncomfortable symptoms. Itching and redness are a result of the body’s attempt to combat the fungal invasion, while increased discharge is often the body’s way of flushing out the intruder. Unfortunately, these defensive mechanisms can become overwhelming, especially if the infection is not treated promptly or appropriately.
Identifying the exact cause and nature of the infection is critical. For instance, recurrent yeast infections—defined as four or more episodes per year—may indicate an underlying health issue or the presence of non-albicans species of Candida, which are more resistant to common treatments. In such cases, the choice of an anti fungal vaginal cream must be informed by lab cultures and susceptibility testing to ensure effective relief.
How Anti Fungal Vaginal Cream Works to Restore Vaginal Health
Antifungal vaginal creams function by directly targeting the fungal cells responsible for the infection, usually without significantly altering the surrounding healthy vaginal flora. The most commonly used antifungal agents in these creams include clotrimazole, miconazole, and tioconazole. Each of these belongs to the azole class of antifungal medications and works by disrupting the synthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes. Without ergosterol, fungal cells lose their integrity and die, effectively stopping the infection.
The application of an antifungal cream for private parts is typically localized to the vulva and intravaginal area, depending on the formulation. Intravaginal creams often come with applicators that help insert the medication deep into the vaginal canal, ensuring that the antifungal agent reaches the site of infection. This targeted delivery allows for rapid symptom relief, often within the first 24 to 48 hours, although complete eradication of the infection may require several days.
One of the advantages of using an anti fungal vaginal cream over oral treatments is the minimal systemic absorption, which reduces the likelihood of side effects or drug interactions. This makes them an excellent choice for individuals with sensitive stomachs, those taking multiple medications, or pregnant women under medical supervision. Additionally, topical creams can also soothe the external irritation and itching that oral treatments may not directly address.
Some formulations include additional ingredients such as hydrocortisone to reduce inflammation or soothing agents like aloe vera and vitamin E to help calm irritated tissue. While these additives can enhance comfort, they should be used cautiously in individuals prone to allergic reactions or skin sensitivity. Always review the product’s ingredient list and consult a healthcare provider if you have a history of dermatitis or other skin conditions.
Ultimately, the goal of an anti fungal vaginal cream is not only to eliminate the immediate symptoms but also to restore the natural microbial equilibrium of the vaginal environment. With appropriate use, these treatments can help prevent recurrent infections and support overall genital health, but they must be selected and applied thoughtfully to achieve optimal results.

Factors to Consider When Choosing an Anti Fungal Vaginal Cream
Selecting the right antifungal cream for private parts requires a comprehensive understanding of one’s symptoms, medical history, and preferences. One of the first considerations should be the severity and frequency of the symptoms. Mild infections may respond well to single-dose treatments, whereas more persistent or recurrent infections often necessitate longer courses of therapy. Misjudging the intensity of the infection can lead to treatment failure or recurrence, emphasizing the importance of accurate assessment.
The active ingredient in the cream plays a central role in its effectiveness. While clotrimazole and miconazole are commonly available over-the-counter, more potent agents like butoconazole or terconazole may require a prescription. These latter medications are often used for more resistant infections or when prior treatments have failed. Additionally, individuals with a history of non-albicans Candida infections may need an entirely different therapeutic approach, as these strains often exhibit resistance to standard azole medications.
Formulation and delivery method also matter. Some creams are thicker and designed for external use only, while others are thinner and meant for intravaginal application. Applicators may be prefilled for convenience or require manual filling. Women who are uncomfortable with inserting medication or who experience vaginal dryness may prefer creams that come with smooth, ergonomic applicators. Others may opt for combination treatments that include both intravaginal cream and external ointment for comprehensive coverage.
Allergies and sensitivities are another important consideration. Some products contain fragrances, dyes, or preservatives that can irritate sensitive skin or trigger allergic reactions. Choosing a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic product can minimize these risks. If you’ve experienced a reaction to a medication in the past, it is essential to verify that the same or a related ingredient is not present in your chosen cream.
Cost, accessibility, and brand reputation may also influence decision-making. While many generic versions of antifungal creams are available at lower prices, brand-name products may offer superior applicators or enhanced formulations with additional skin-soothing ingredients. Insurance coverage, pharmacy availability, and personal preference all factor into the final choice, underscoring the individualized nature of effective treatment selection.
Evaluating the Best Antifungal Cream for Private Area Relief
When seeking the best antifungal cream for private area infections, efficacy, tolerability, and ease of use are key benchmarks. Many over-the-counter antifungal creams have undergone rigorous clinical testing and demonstrated comparable effectiveness, but individual response can vary significantly. Clotrimazole 1% and miconazole 2% remain two of the most commonly recommended ingredients, often favored for their wide availability and robust track record in clearing uncomplicated infections.
However, the frequency of application and duration of treatment differ among products. For instance, clotrimazole-based creams may be offered in both one-day and seven-day formulations. While the one-day treatment may appeal to those looking for fast relief, the seven-day option tends to be gentler and more thorough, making it a better choice for those with sensitive skin or moderate symptoms. Tioconazole, typically available in one-day doses, is a more concentrated formula that offers convenience but may cause more irritation in some users.
Prescription-strength creams such as terconazole 0.4% or 0.8% are often used for infections that are recurrent or resistant to standard treatments. These are particularly effective in patients with underlying medical conditions that predispose them to chronic yeast infections, such as diabetes or immune suppression. Though more expensive, they are often covered by insurance and come with the added benefit of medical oversight during treatment.
The inclusion of soothing agents in some of the best antifungal creams for private area relief has revolutionized comfort during treatment. Products that include vitamin E, aloe vera, or chamomile can significantly reduce external itching and redness. However, individuals should be cautious about creams that list alcohols or unnecessary preservatives, which can exacerbate discomfort rather than alleviate it.
Beyond ingredients and formulation, practical aspects such as packaging, applicator quality, and ease of cleanup also play a role in determining the best product for individual needs. Some women prefer pre-filled disposable applicators for hygiene and simplicity, while others appreciate reusable options for their environmental benefits. With such variability in preferences and responses, trying different products—under medical guidance when needed—can help identify which cream offers the most reliable and comfortable relief.
Applying Anti Fungal Vaginal Cream Correctly for Optimal Results
Correct application of an anti fungal vaginal cream is fundamental to its effectiveness. Despite the accessibility of over-the-counter treatments, many women unknowingly reduce the efficacy of these creams through inconsistent or improper usage. To begin, it’s crucial to understand that antifungal creams for private parts are intended to be used consistently over the entire recommended duration, even if symptoms begin to resolve earlier. Stopping treatment prematurely can lead to incomplete eradication of the fungus and pave the way for recurrent infections.
Before applying the cream, one should thoroughly wash their hands and the external genital area with mild, fragrance-free soap and warm water. This not only ensures cleanliness but also removes excess discharge or sweat that may interfere with the cream’s absorption. Once dried gently with a clean towel, the user should lie on their back with knees bent—ideally in a relaxed environment to reduce muscle tension and facilitate smooth application.
If the product includes an applicator, it should be filled as per the instructions provided and gently inserted into the vagina until resistance is felt. The cream is then released slowly to coat the internal surfaces evenly. This intravaginal application targets the infection at its source and is usually done before bedtime to prevent leakage due to gravity and ensure prolonged contact with the mucosal tissue. For external itching and irritation, a small amount of cream should be applied to the vulva and surrounding area, avoiding excessive pressure or rubbing.
Users should always refer to the enclosed leaflet for specific product instructions, as concentrations and ingredients can vary across brands. Some creams may require once-daily application, while others are designed for use twice a day. Missing doses or substituting with different products mid-treatment can reduce effectiveness and potentially lead to resistance.
It’s also important to note that sexual activity should be avoided during treatment, as intercourse can irritate the vaginal tissues further and reduce the cream’s efficacy. Additionally, some antifungal creams may weaken latex condoms or diaphragms, increasing the risk of contraceptive failure or STI transmission. By understanding these nuances and adhering to correct usage, women can maximize the therapeutic benefits of their chosen anti fungal vaginal cream and promote faster recovery.

Understanding Recurrent Infections and Long-Term Management Strategies
Recurrent vaginal yeast infections are not only frustrating but also indicative of an underlying imbalance that may not be resolved by short-term treatment alone. Defined as four or more infections within a 12-month period, recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis often requires a deeper investigation into possible triggers and a longer-term management plan. For many women, lifestyle factors, immune status, hormonal fluctuations, and microbiota imbalances contribute to this chronic cycle.
Women experiencing recurrent infections should consider getting a vaginal culture to identify the specific Candida species involved. While Candida albicans is the most common culprit and usually responds well to standard azole antifungals, non-albicans species such as Candida glabrata are more resistant and may require different treatment approaches, such as boric acid suppositories or nystatin. Knowing the pathogen’s identity can significantly enhance the precision of antifungal therapy and reduce recurrence rates.
Beyond the choice of antifungal cream for private parts, long-term strategies often include dietary modifications, such as reducing refined sugars and carbohydrates that may feed yeast growth. Probiotic supplementation—either orally or vaginally—can help replenish Lactobacillus levels and restore a more balanced vaginal microbiome. Some women find that wearing breathable cotton underwear and avoiding scented hygiene products also contributes to fewer flare-ups.
Hormonal factors also warrant close examination. Women on hormonal contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy may experience changes in vaginal pH that favor fungal growth. In these cases, collaboration with a healthcare provider to adjust dosages or switch formulations may help reduce the risk of recurrent infections. Similarly, managing conditions like diabetes with strict glycemic control can dramatically lower the incidence of yeast infections by depriving Candida of excess glucose.
For those with persistent issues, maintenance therapy may be recommended. This could involve weekly application of a low-dose anti fungal vaginal cream or intermittent oral antifungal medication under medical supervision. Such strategies help prevent the overgrowth of yeast while minimizing the risk of resistance. Ultimately, the path to lasting relief from recurrent infections is multifaceted, requiring both medical and lifestyle interventions tailored to the individual’s unique health profile.
Choosing an Anti Fungal Vaginal Cream During Pregnancy or Breastfeeding
Pregnancy introduces additional complexities when treating vaginal yeast infections, making the selection of an appropriate anti fungal vaginal cream a matter of heightened caution. Hormonal changes during pregnancy naturally alter the vaginal environment, making pregnant individuals more susceptible to fungal overgrowth. The increased estrogen levels and glycogen production create ideal conditions for Candida to thrive, often resulting in more frequent and intense infections.
Fortunately, most anti fungal creams are considered safe for use during pregnancy, particularly when used under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Clotrimazole and miconazole are the most frequently recommended agents, supported by extensive clinical research affirming their safety profiles when applied topically. These medications do not show evidence of teratogenic effects and are preferred over oral antifungal treatments, which may carry more significant systemic risks.
The preferred regimen during pregnancy is typically a 7-day course, which allows for a gentler yet thorough resolution of the infection. Shorter-duration, high-dose treatments may cause irritation and are less commonly recommended for expectant mothers. Creams with mild formulations and without strong preservatives or fragrances are ideal, as pregnant individuals may experience increased skin sensitivity.
Application techniques should remain gentle and cautious, avoiding undue pressure or deep insertion, especially during the later stages of pregnancy. It’s also advisable to consult an obstetrician before beginning any antifungal treatment to ensure it aligns with the overall pregnancy care plan. Some women may experience yeast infections in conjunction with other pregnancy-related issues, such as gestational diabetes, which further complicates treatment selection and underscores the importance of professional oversight.
For breastfeeding individuals, the concern is not so much the topical application itself, but the possibility of infants coming into contact with medicated skin. Most anti fungal creams for private parts are used in areas not involved in breastfeeding, making them safe for postpartum use as well. Nonetheless, careful hand hygiene after application and avoiding contact between the treated area and the baby are prudent precautions. In every case, transparency with healthcare providers ensures that both maternal and infant health are prioritized during treatment.
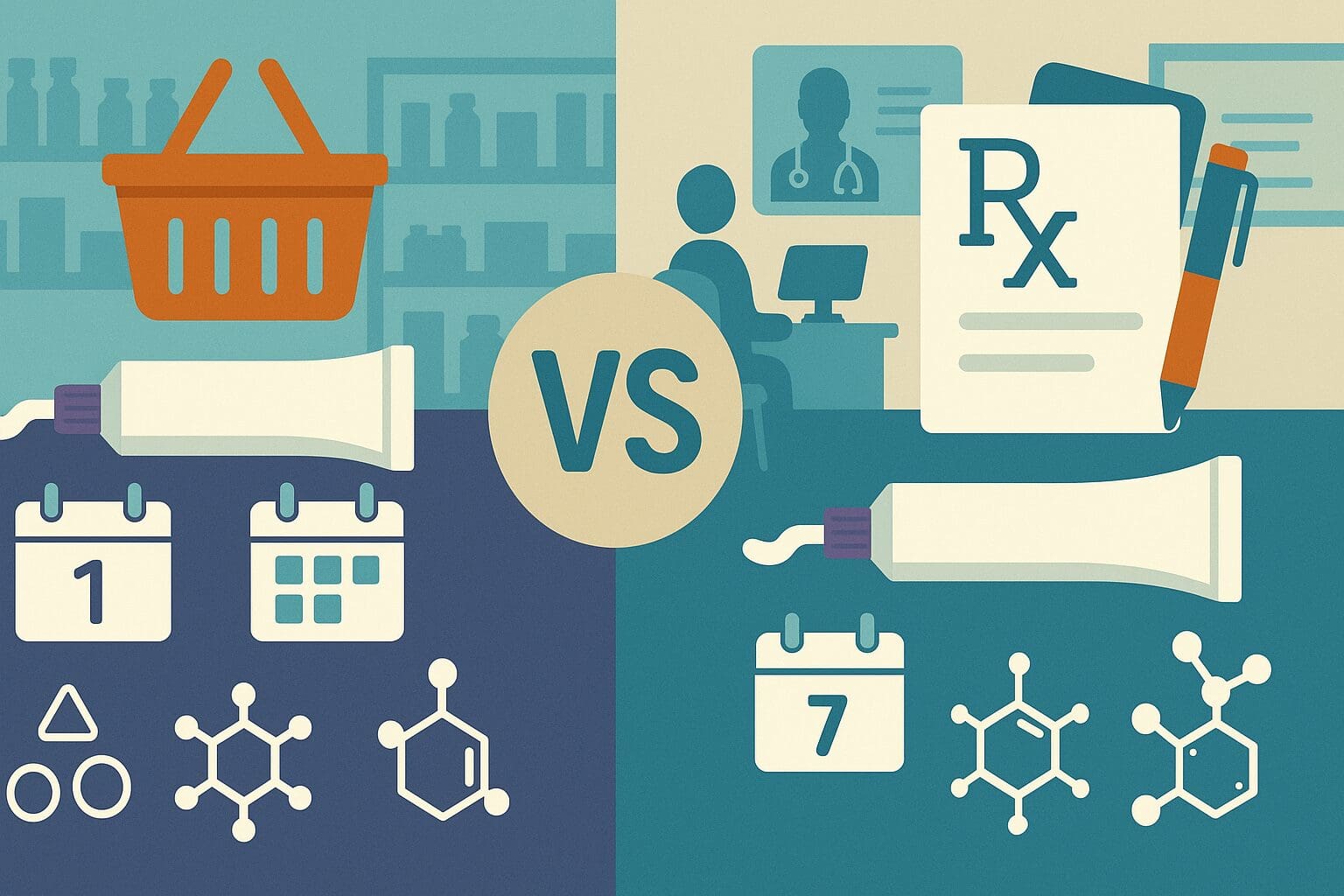

Comparing Over-the-Counter and Prescription Options
The marketplace for antifungal creams is divided broadly into two categories: over-the-counter (OTC) options and prescription medications. While OTC anti fungal vaginal cream products are widely available and effective for most uncomplicated infections, prescription-strength treatments are often necessary for more severe or resistant cases. Understanding the differences between these categories can guide women in selecting the most appropriate remedy.
OTC creams generally contain clotrimazole, miconazole, or tioconazole, and are available in one-day, three-day, or seven-day treatment regimens. These options are ideal for individuals who have previously had a diagnosed yeast infection and are experiencing a recurrence with familiar symptoms. They offer a high degree of convenience and affordability and can be purchased without a doctor’s visit. However, they are not suitable for every situation, especially if symptoms persist or worsen after initial treatment.
Prescription creams, on the other hand, often include more potent antifungal agents such as terconazole or butoconazole. These medications may come in higher concentrations or offer extended-release formulations for sustained action. Physicians may recommend prescription creams after conducting a pelvic exam or culture to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. This level of specificity ensures more targeted treatment, particularly in women who have not responded to standard therapy.
Another benefit of prescription creams is the ability to tailor the formulation to the patient’s unique needs. For example, individuals with known allergies to azoles may be prescribed alternative antifungal agents. Additionally, some prescription formulations come with adjunctive ingredients to reduce inflammation or restore vaginal flora, providing a more holistic approach to treatment.
Cost is an important consideration, as prescription medications can be more expensive upfront but are often covered by insurance. Conversely, OTC products are accessible but may lead to higher cumulative costs if multiple unsuccessful attempts are made to resolve a persistent infection. Consulting a healthcare provider can help clarify which path is more appropriate based on the severity of symptoms, medical history, and overall health status.
How to Differentiate Yeast Infections from Other Vaginal Conditions
Misdiagnosis is one of the most common reasons why women fail to achieve relief from antifungal treatments. Although the symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection are often distinctive, they can closely mimic those of other conditions, including bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, herpes simplex virus, and even dermatological issues like contact dermatitis. Understanding the differences can prevent unnecessary treatment delays and avoid complications.
Bacterial vaginosis (BV), for instance, also presents with vaginal discharge, but the discharge in BV is typically thin, grayish, and accompanied by a strong, fishy odor—features not commonly found in yeast infections. BV is caused by an overgrowth of anaerobic bacteria and requires antibiotic treatment, making antifungal creams ineffective. Treating BV with an antifungal cream may temporarily mask some symptoms but will not resolve the underlying problem.
Trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by a protozoan parasite, also produces discharge and irritation but is usually associated with a frothy, yellow-green discharge and often a burning sensation during urination. Trichomoniasis requires treatment with specific antiparasitic medication such as metronidazole, again rendering antifungal therapies useless in such cases.
In some cases, women may experience allergic reactions or irritant contact dermatitis due to hygiene products, laundry detergents, or even certain fabrics. These reactions can lead to itching, redness, and swelling that are easily confused with yeast infections. However, these conditions are non-infectious and typically respond to corticosteroids or antihistamines, not antifungal agents.
Herpes simplex virus outbreaks can also present as intense vulvar itching and burning, particularly before lesions appear. This makes it critical to consider a broader range of symptoms and, if necessary, undergo diagnostic testing to rule out viral causes. For those who are uncertain or experiencing symptoms for the first time, seeking professional evaluation before using any anti fungal vaginal cream is a wise step.
Accurate diagnosis ensures that the selected treatment matches the underlying cause of symptoms. This not only prevents prolonged discomfort but also avoids the unnecessary use of medications that may disrupt the natural balance of the vaginal environment or contribute to resistance in the case of recurrent infections.

Expert Tips for Preventing Future Yeast Infections
While antifungal creams offer effective relief, prevention remains the most sustainable strategy for long-term vaginal health. Experts emphasize that lifestyle modifications, personal hygiene, and awareness of bodily changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing yeast infections. These interventions, while simple, require consistency and attentiveness.
One of the most impactful preventive measures is maintaining a healthy vaginal pH. This can be supported by avoiding douching, which disrupts the natural acidic environment, and using gentle, fragrance-free soaps around the genital area. Regular cleansing with water and patting the area dry rather than rubbing helps maintain the delicate balance of the vulvar skin. Wearing breathable cotton underwear and avoiding prolonged use of tight-fitting clothing can reduce moisture buildup, a key factor in Candida overgrowth.
Dietary adjustments can also play a meaningful role in prevention. Diets high in refined sugar and processed carbohydrates may create conditions favorable to fungal growth, particularly in women with insulin resistance or poorly managed diabetes. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can help maintain healthy bacterial populations in the gut and vaginal tract. Some women also choose to take daily probiotic supplements specifically designed for vaginal health.
Hormonal regulation is another preventive cornerstone. Women undergoing hormonal therapy or those who experience infections aligned with specific phases of their menstrual cycle may benefit from tracking symptoms and discussing adjustments with their healthcare provider. Birth control methods that significantly alter estrogen levels might need to be reconsidered if they are contributing to recurrent yeast infections.
Finally, managing stress and supporting immune function are crucial, as chronic stress can suppress immune response and predispose the body to infections. Getting adequate sleep, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness or yoga can enhance the body’s natural defenses. These holistic strategies, when combined with timely and accurate treatment using an anti fungal vaginal cream, create a comprehensive defense against future infections.
Frequently Asked Questions: Expert Insights on Using Anti Fungal Vaginal Cream Safely and Effectively
1. How do I know if an anti fungal vaginal cream is the right choice for recurring infections?
While an anti fungal vaginal cream can provide fast relief from common symptoms like itching, burning, and discharge, it’s not always the complete solution for recurrent infections. Women who experience frequent flare-ups—more than four times a year—may have an underlying condition such as diabetes, hormonal imbalances, or antibiotic overuse that contributes to yeast overgrowth. In these cases, a cream alone may mask symptoms without addressing the root cause. It’s wise to consult a gynecologist to discuss systemic antifungal treatments or vaginal flora restoration therapies, including probiotics. Customizing your care plan with lifestyle changes and preventive strategies can improve long-term outcomes.
2. Can I use an antifungal cream for private parts during my period?
Using an antifungal cream for private parts during menstruation is possible, but there are practical and medical considerations. Menstrual blood can dilute the medication, reducing its effectiveness, especially if it’s a topical cream meant to stay in place. Tampons may also interfere with absorption or cause added irritation if used simultaneously. In some cases, physicians may recommend postponing treatment until the period ends, or switching to oral antifungals during that time. If symptoms are severe, dual-use with pads instead of tampons may help maintain cream efficacy. Always follow the medication’s instructions and check with your healthcare provider for specific guidance based on the product formulation.
3. What lifestyle habits can improve the effectiveness of anti fungal vaginal cream?
To boost the results of an anti fungal vaginal cream, certain daily habits can make a meaningful difference. Wearing breathable, cotton underwear helps reduce moisture that encourages fungal growth. Avoiding scented soaps, tight-fitting synthetic fabrics, and prolonged wetness (like sitting in a damp swimsuit) can minimize recurrence. A balanced diet low in sugar and high in fiber supports immune function and reduces yeast-promoting conditions. Stress management is also critical, as chronic stress can disrupt vaginal pH and immunity. Pairing good hygiene with these habits can make your antifungal regimen more successful and reduce your reliance on repeated applications.
4. Why does antifungal cream for private parts sometimes cause a burning sensation?
A mild burning or stinging sensation when applying antifungal cream for private parts is a fairly common side effect, especially if the skin is already inflamed or cracked. This sensation typically subsides within a few minutes as the cream absorbs. However, if burning persists or worsens, it could indicate a sensitivity to an inactive ingredient or a misdiagnosis—like bacterial vaginosis or an allergy rather than a yeast infection. Avoid using additional products like douches or wipes that could further irritate the area. Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures the reaction isn’t due to misuse or an alternative condition requiring different treatment.
5. Are there alternatives to anti fungal vaginal cream for those with sensitive skin?
Yes, women with sensitive skin or allergies to certain cream ingredients can explore several alternative treatments. Vaginal suppositories that dissolve internally may bypass external irritation altogether. Prescription oral antifungals like fluconazole are also effective and do not involve topical application. Some natural approaches, such as using boric acid capsules or probiotic vaginal inserts, have shown promise in managing chronic yeast infections, especially when used under medical supervision. If over-the-counter creams cause discomfort, ask your doctor about hypoallergenic formulas specifically designed for sensitive skin, which typically exclude common irritants like parabens, alcohol, or fragrances.
6. What makes the best antifungal cream for private area different from generic options?
The best antifungal cream for private area use is often distinguished by its formulation, pH balance, and targeted delivery system. Premium products typically contain soothing ingredients like aloe vera or calendula, which minimize irritation while still delivering potent antifungal agents. They may also be gynecologist-tested for safety in the vulvovaginal region, ensuring better compatibility with sensitive tissues. In contrast, generic or multipurpose antifungal creams might be too harsh or oily, leading to discomfort or an altered vaginal pH. Investing in a product made specifically for intimate areas helps ensure both effectiveness and comfort, particularly for those with recurring issues.
7. Can anti fungal vaginal cream be used preventatively?
While not typically recommended for daily use, some women under medical supervision may use anti fungal vaginal cream preventatively in specific scenarios. For example, women prone to yeast infections following antibiotic use may apply the cream at the first sign of irritation to ward off a full-blown infection. Similarly, during hormone shifts—like those caused by pregnancy or fertility treatments—doctors may advise intermittent preventative use. However, regular application without symptoms can disrupt the natural balance of vaginal flora and increase resistance. Always consult a doctor before initiating a preventive regimen to avoid inadvertently triggering further complications.
8. How do I maintain healthy vaginal flora after using anti fungal vaginal cream?
Restoring and maintaining a healthy vaginal microbiome after treatment is critical for preventing future infections. Taking probiotics that include Lactobacillus strains can help reestablish a protective bacterial balance. Avoiding unnecessary antibiotics, choosing mild, pH-balanced cleansers, and practicing safe sex can also contribute to flora stability. Some women benefit from incorporating vaginal probiotic suppositories or fermented foods into their routine. While anti fungal vaginal cream resolves symptoms quickly, it does not repopulate beneficial bacteria, making these follow-up steps essential for long-term health.
9. What innovations are emerging in antifungal cream for private parts?
The next generation of antifungal cream for private parts is focused on targeted delivery and enhanced biocompatibility. Nanotechnology is being explored to improve drug penetration and reduce dosing frequency. Additionally, researchers are developing bioadhesive gels that stay in place longer and release medication gradually. New formulations are also integrating pH-stabilizing components that simultaneously treat and prevent recurrence. Companies are increasingly prioritizing hypoallergenic, fragrance-free options that address the unique challenges of sensitive skin. These advancements aim to make treatments more effective, user-friendly, and aligned with the needs of modern vaginal health management.
10. How can I safely choose the best antifungal cream for private area use without a prescription?
To select the best antifungal cream for private area use without a prescription, pay close attention to active ingredients and intended usage. Products containing clotrimazole or miconazole are widely recommended for mild to moderate yeast infections and are generally safe for self-use. Look for packaging that specifies “gynecologist-tested” or “formulated for vaginal use” to avoid applying harsh agents designed for feet or skin folds. Reading customer reviews can also provide insight into comfort, effectiveness, and user satisfaction. However, if symptoms don’t improve within three days or worsen, it’s essential to discontinue use and seek professional medical evaluation.
Final Thoughts: Empowering Vaginal Health with the Right Anti Fungal Vaginal Cream
Navigating the landscape of intimate health can feel overwhelming, particularly when symptoms of discomfort and irritation arise unexpectedly. However, with the right knowledge and tools, women can take empowered steps toward healing and prevention. Choosing the appropriate anti fungal vaginal cream is not just about immediate symptom relief; it’s about restoring the body’s natural balance and understanding the conditions that allowed the infection to take hold in the first place.
A thoughtful approach begins with recognizing the signs of a yeast infection and distinguishing them from other possible conditions. From there, selecting a cream with the right active ingredients, formulation, and delivery method can make a substantial difference in both comfort and outcome. Whether opting for a mild over-the-counter cream or requiring a prescription-strength treatment, the focus should always be on safe, effective, and personalized care.
Moreover, addressing underlying factors such as hormone fluctuations, dietary habits, hygiene routines, and stress levels can reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Combining medical treatment with lifestyle adjustments ensures that vaginal health is supported in a sustainable, holistic way. This integrative approach also fosters a deeper awareness of one’s body, making it easier to detect imbalances early and respond with confidence.
Ultimately, the journey toward vaginal well-being is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Each woman’s body is unique, and so are her needs when it comes to treatment. By leveraging scientifically backed information, expert insights, and personal awareness, women can make informed choices that support both immediate healing and long-term health. An anti fungal vaginal cream, when chosen wisely, can be a powerful ally in this journey—offering not only relief but also a renewed sense of comfort and control over one’s intimate health.



