Introduction: The Foundation of Everyday Wellness for Women
Achieving vibrant, long-lasting health requires more than occasional self-care or sporadic exercise—it demands intentional daily nourishment that aligns with a woman’s unique biological and lifestyle needs. In this context, focusing on essential nutrition tips to support womens daily health goals becomes not just a matter of dietary choice but a strategy for sustaining energy, mood, hormonal balance, and long-term disease prevention. The human body—particularly the female body—requires specific nutrients in particular ratios to function at its peak across every stage of life, from menstruation and pregnancy to menopause and beyond. Whether you’re a college graduate entering the workforce or a seasoned professional balancing career, family, and personal ambitions, adopting the right nutritional strategies is critical for mental clarity, immunity, reproductive health, and vitality.
Unlike one-size-fits-all diets or temporary detoxes that fade with time, sustainable nutrition builds a physiological and psychological foundation that enhances resilience. Women are often at the nexus of multitasking, caregiving, and professional excellence, which places additional strain on their nutritional reserves. This makes consistent, informed dietary decisions not just ideal—but necessary. It’s not enough to simply eat a “balanced” meal. Women need to understand how micronutrients, macronutrients, and hormonal fluctuations interplay with their nutritional status on a day-to-day basis. By exploring expert-backed strategies for optimizing health through intentional eating, this article equips readers with the tools to thrive across every dimension of daily life.
You may also like: 10 Essential Nutrition Rules to Follow for a Healthy Diet for Women in 20s
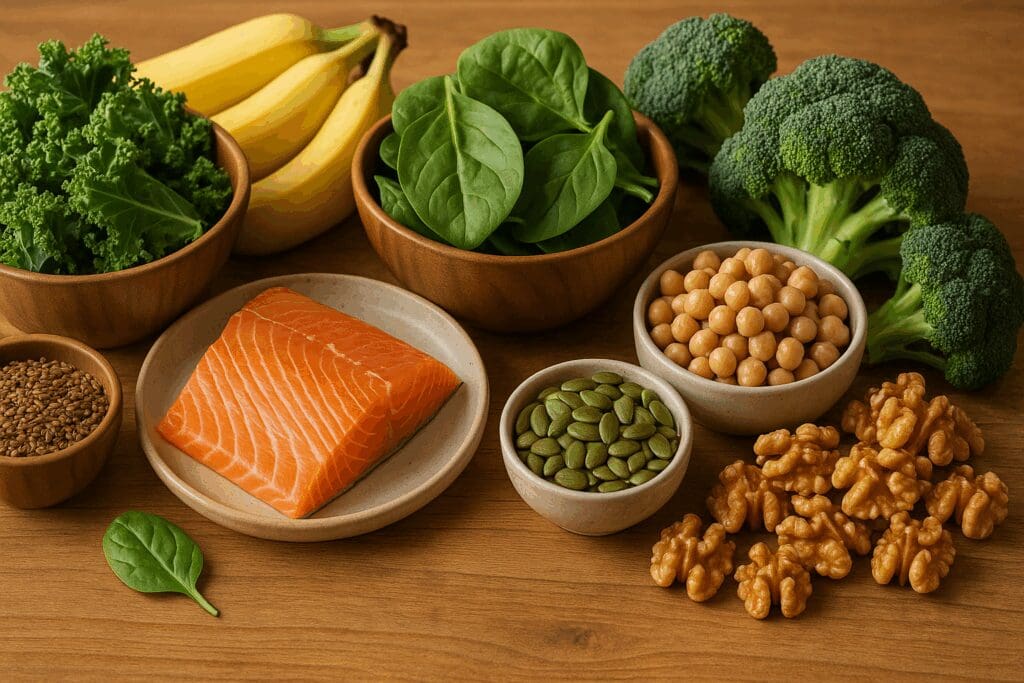

Prioritizing Nutrient-Dense Foods for Hormonal Harmony
One of the foundational pillars of womens daily health involves balancing hormonal rhythms through nutrient-dense eating. Unlike restrictive diets that deprive the body of essential building blocks, focusing on nutrient-dense foods ensures that women obtain ample vitamins, minerals, phytonutrients, and antioxidants needed to fuel cellular regeneration and hormonal synthesis. Hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and cortisol are all influenced by dietary patterns, and imbalances in these can lead to fatigue, mood swings, irregular menstrual cycles, and weight fluctuations.
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids—such as wild-caught salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts—support hormone production by providing anti-inflammatory essential fats. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale contain compounds such as indole-3-carbinol that aid in estrogen metabolism, preventing dominance or deficiency. In parallel, foods high in vitamin B6 and magnesium—such as chickpeas, bananas, and pumpkin seeds—support neurotransmitter balance and reduce PMS-related symptoms. It’s also essential to consume adequate protein from both animal and plant sources to ensure that amino acids are available for building hormones and repairing tissues.
Equally vital is reducing the intake of highly processed foods, trans fats, and added sugars that can interfere with insulin sensitivity and exacerbate estrogen imbalances. A nutrient-dense plate is colorful and varied, emphasizing fresh produce, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. In essence, each meal should be seen not just as sustenance but as an opportunity to restore biochemical equilibrium, particularly during periods of stress or hormonal transition.

Managing Energy Levels Through Macronutrient Timing
Sustained energy is essential for productivity, focus, and physical activity—three elements that define womens daily routines across all ages and lifestyles. While caffeine may offer a temporary boost, true energy balance is rooted in how the body metabolizes macronutrients throughout the day. This includes carbohydrates, fats, and proteins—each playing a unique role in energy production, hormonal regulation, and satiety.
A common issue many women face is blood sugar instability, often caused by erratic eating patterns or carbohydrate-heavy meals lacking protein or fiber. To prevent crashes in energy and mood, meals should be designed to stabilize glucose levels by combining complex carbohydrates—like quinoa or sweet potatoes—with protein and healthy fats. For example, a breakfast of Greek yogurt, chia seeds, and berries provides a powerful mix of slow-digesting carbohydrates, complete protein, and omega-3 fats that support metabolic stability throughout the morning.
Equally important is the timing of meals and snacks. Skipping meals can disrupt the body’s circadian rhythms and impair cortisol patterns, leading to fatigue and cravings. Eating within 30 to 60 minutes of waking supports the adrenal system, while spreading meals every three to four hours helps maintain steady energy. Women engaging in high levels of activity or intense mental labor may benefit from small, nutrient-rich snacks like hard-boiled eggs or almond butter with apple slices to bridge gaps between meals and sustain focus.
Furthermore, hydration plays a subtle but critical role in energy regulation. Dehydration can mimic fatigue, slow cognitive processing, and impair digestion. Women should aim to drink at least 2 to 2.5 liters of water daily, adjusting for climate, exercise, and caffeine intake. Infusing water with citrus or cucumber can also encourage greater fluid intake while supplying trace electrolytes.
Womens Daily Health Goals and Bone Strength Across Life Stages
Strong bones are foundational to physical independence, particularly as women age and face the increased risk of osteoporosis. Calcium and vitamin D are well-known players in bone health, but they are only part of a broader symphony of nutrients needed to maintain skeletal integrity across every decade of life. For womens daily nutritional needs, supporting bone density involves a multifaceted approach that combines diet, movement, and strategic supplementation.
Calcium-rich foods like leafy greens, fortified plant milks, yogurt, and tofu should be regularly incorporated into meals. However, without adequate vitamin D—acquired through sun exposure or supplements—the body cannot efficiently absorb dietary calcium. Magnesium, vitamin K2, and boron also play critical roles in guiding calcium into the bone matrix and ensuring that it remains there, rather than accumulating in soft tissues. Foods like avocados, dark chocolate, and fermented soy provide these often-overlooked cofactors.
During adolescence and early adulthood, peak bone mass is established, making these years essential for developing strong skeletal foundations. In later decades, especially post-menopause, declining estrogen levels increase bone turnover and heighten fracture risk. This necessitates not just continued intake of bone-supportive nutrients but also engagement in weight-bearing exercises such as walking, resistance training, and Pilates. These activities stimulate bone remodeling and increase muscle mass, which further protects the joints.
It’s also crucial to limit excessive alcohol and sodium, both of which can leach calcium from the bones and impair hormonal regulation. For women who follow vegan diets or have lactose intolerance, thoughtful planning is essential to ensure that plant-based calcium sources are adequately paired with absorption-enhancing nutrients. Working with a dietitian can also help identify hidden deficiencies or tailor a supplement regimen that complements dietary patterns.

The Gut Microbiome’s Role in Womens Daily Health
Recent advances in nutritional science have shed light on the immense role that gut health plays in overall wellbeing, from immunity to mood regulation and hormone metabolism. For women, maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is especially significant, as fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone can directly impact gut permeability and microbial diversity. Prioritizing gut health is therefore a key strategy in supporting womens daily health and ensuring resilience across menstrual cycles, pregnancy, perimenopause, and beyond.
A diverse, fiber-rich diet is the cornerstone of microbiome integrity. Soluble and insoluble fibers found in legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables serve as prebiotics—compounds that feed beneficial gut bacteria. These bacteria, in turn, produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate that reduce inflammation, enhance immune response, and fortify the intestinal barrier. Fermented foods such as kimchi, sauerkraut, kefir, and miso provide probiotics that introduce beneficial strains of bacteria and support microbial balance.
Gut dysbiosis—a disruption in healthy bacteria—has been linked to conditions more prevalent in women, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and autoimmune thyroid disorders. These associations emphasize the importance of dietary choices in regulating systemic inflammation and endocrine health. For instance, excessive intake of artificial sweeteners, antibiotics, and processed foods can damage microbial diversity and impair gut function. Conversely, anti-inflammatory nutrients like curcumin, polyphenols from berries, and omega-3s can help restore equilibrium.
Supporting digestion also involves mindful eating habits such as chewing food thoroughly, avoiding overeating, and spacing meals to allow for digestive rest. Some women may benefit from targeted supplementation with digestive enzymes or spore-based probiotics, especially during times of stress, travel, or after antibiotic use. While individualized approaches are ideal, general practices that prioritize gut-friendly nutrition benefit nearly all women in their daily pursuit of energy, clarity, and hormonal harmony.

Navigating Iron, B12, and Folate for Womens Daily Vitality
Micronutrients like iron, vitamin B12, and folate are especially important in a woman’s nutritional landscape, impacting everything from red blood cell production to cognitive performance and reproductive health. These nutrients are particularly vital during menstruating years, pregnancy, and periods of intense physical or mental exertion. Because of menstrual blood loss, women have higher daily iron needs than men, and deficiencies can manifest as fatigue, pale skin, brittle nails, and impaired immunity—issues that subtly erode daily quality of life if left unaddressed.
Iron comes in two forms: heme iron found in animal sources like red meat and poultry, and non-heme iron found in plant sources such as lentils, spinach, and fortified cereals. While both are beneficial, heme iron is more readily absorbed. Women following plant-based or vegetarian diets must be especially diligent, as non-heme iron is more susceptible to absorption inhibitors like calcium and phytates. Pairing plant-based iron with vitamin C-rich foods—like citrus, bell peppers, or strawberries—enhances bioavailability and promotes absorption.
Vitamin B12 and folate work closely together to support DNA synthesis and nervous system health. Deficiency in either can lead to megaloblastic anemia, neurological changes, and reproductive challenges. B12 is naturally found in animal products such as eggs, dairy, and seafood, making supplementation critical for vegans. Folate, on the other hand, is found in leafy greens, legumes, and citrus fruits but can be compromised by poor digestion or genetic variations such as MTHFR mutations, which impair conversion of folic acid into its active form.
Routine lab testing can help women monitor their iron status, ferritin levels, and B12 sufficiency, especially if they experience persistent fatigue or are planning a pregnancy. Methylated forms of B12 and folate can offer enhanced absorption for those with absorption difficulties. Ensuring optimal levels of these micronutrients fortifies the body’s ability to deliver oxygen, synthesize neurotransmitters, and support fetal development during conception and pregnancy, reinforcing their central role in womens daily health.
Emphasizing Omega-3s and Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition
Chronic inflammation, even at low levels, is a silent contributor to many conditions that disproportionately affect women, including autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular disease, and arthritis. Diets rich in processed foods, industrial seed oils, and added sugars can fuel this inflammation, whereas anti-inflammatory eating patterns offer a powerful counterbalance. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids and polyphenol-rich plants provides a strategic advantage for reducing oxidative stress, supporting cardiovascular function, and improving mood.
Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically EPA and DHA, are primarily found in cold-water fish like sardines, mackerel, and salmon. For plant-based eaters, algae-based supplements offer a bioavailable vegan alternative. These fats play a key role in moderating inflammatory pathways, supporting brain health, and enhancing cellular communication. Numerous studies also suggest that adequate omega-3 intake reduces the severity of menstrual pain and lowers the risk of postpartum depression.
Antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, green tea, turmeric, ginger, and dark leafy greens provide further anti-inflammatory support. These compounds neutralize free radicals and modulate the expression of genes involved in inflammation. Moreover, spices like turmeric—when combined with black pepper for enhanced bioavailability—act as natural COX-2 inhibitors, reducing pain and stiffness without the side effects of NSAIDs.
In addition to what is consumed, what is avoided matters. Reducing refined carbohydrates, deep-fried foods, and excess alcohol limits the activation of inflammatory cascades. Transitioning toward a Mediterranean-style diet or a whole-food, plant-forward eating pattern can lead to substantial improvements in markers of inflammation, particularly for women with autoimmune conditions or metabolic syndrome. By weaving anti-inflammatory principles into womens daily eating habits, long-term resilience and graceful aging are more attainable.
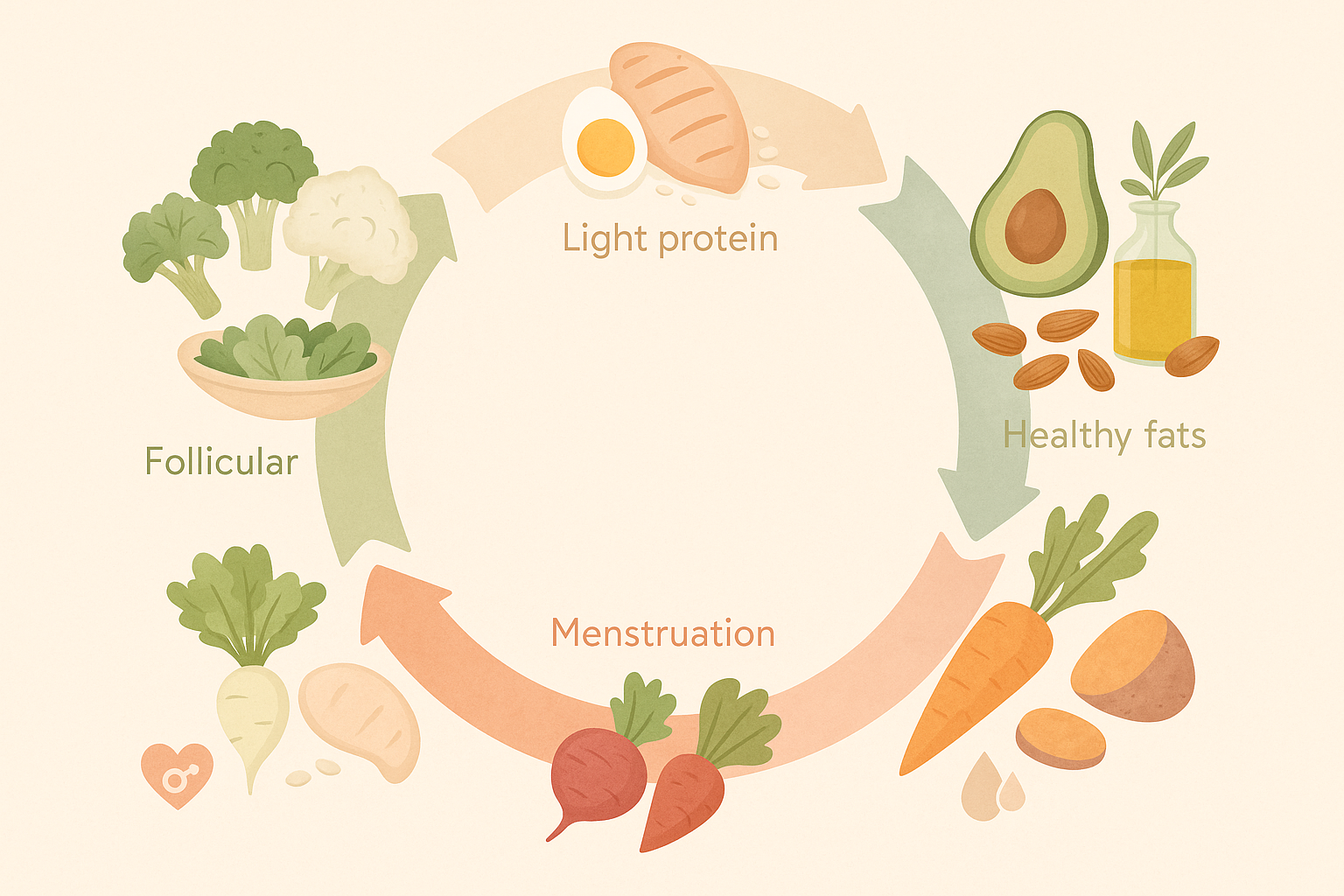
Womens Daily Nutritional Needs During Reproductive Years
The reproductive years—marked by the onset of menstruation and extending through menopause—represent a dynamic and hormonally complex phase that requires precise nutritional attention. During this time, nutrient demands fluctuate due to monthly cycles, pregnancy, lactation, and stress, making it crucial to adopt a flexible yet consistently nourishing approach to food. When hormonal shifts are supported by key nutrients, women are more likely to experience regular cycles, fewer PMS symptoms, and enhanced fertility.
Iron, zinc, and iodine are pivotal minerals during these years. Zinc supports ovulation and immunity, while iodine is necessary for thyroid health and fetal brain development. While dairy, shellfish, and seaweed are natural iodine sources, many women benefit from iodized salt in moderation. Ensuring adequate intake of choline—found in eggs, legumes, and lean meats—is also essential, particularly during pregnancy, when it contributes to fetal neural development and reduces the risk of neural tube defects.
Cycle-syncing nutrition is an emerging strategy gaining traction among integrative health practitioners. This approach tailors food choices to the four phases of the menstrual cycle: follicular, ovulation, luteal, and menstruation. For instance, focusing on cruciferous vegetables and light proteins during the follicular phase supports estrogen clearance, while root vegetables and healthy fats during the luteal phase promote progesterone balance and mood regulation. While not a one-size-fits-all solution, tuning into cyclical rhythms and adjusting food accordingly can enhance energy, cognition, and emotional wellbeing.
Pregnancy introduces another layer of complexity, dramatically increasing the need for iron, folate, omega-3s, and vitamin D. During lactation, energy and protein needs rise to support milk production and maternal recovery. Rather than focusing solely on caloric intake, women should emphasize quality, diversity, and micronutrient density. Prenatal vitamins serve as an important foundation but should never replace a robust, varied diet. Consulting a nutritionist can help create a personalized plan that accommodates changing physiological demands while preventing deficiencies.

Supporting Cognitive Health and Mental Resilience
Mental wellness is a cornerstone of daily functionality, and diet exerts a profound influence on mood regulation, stress tolerance, and cognitive clarity. Women are more likely than men to experience anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders—often exacerbated by hormonal changes and nutrient deficiencies. Recognizing the interplay between food and neurochemistry is essential to supporting cognitive health and emotional balance in womens daily routines.
Tryptophan, an amino acid found in turkey, oats, and seeds, is a precursor to serotonin—the neurotransmitter associated with happiness and relaxation. Adequate protein intake ensures a steady supply of these precursors, while complex carbohydrates facilitate their transport across the blood-brain barrier. Omega-3s, again, play a starring role by supporting neuronal membrane fluidity and enhancing communication between brain cells. A deficiency in DHA, in particular, has been linked to impaired cognition and higher rates of depression.
B vitamins—especially B6, B9 (folate), and B12—are critical for neurotransmitter synthesis, energy metabolism, and homocysteine regulation. Deficiencies can lead to brain fog, irritability, and even memory issues. Including whole grains, leafy greens, eggs, and legumes can help meet these needs, while women with genetic methylation issues may benefit from active forms of these vitamins.
Equally important is blood sugar stability. Rapid spikes and crashes in glucose can trigger anxiety, irritability, and fatigue. Balancing meals with fiber, fat, and protein helps modulate glycemic response and improves mood resilience. Mindful eating practices—such as chewing thoroughly, avoiding distractions, and savoring meals—enhance digestion and promote a parasympathetic nervous system response that reduces cortisol levels. Nutrition for mental health is not a luxury; it’s a daily necessity for thriving in fast-paced, demanding environments.
Womens Daily Hydration Strategies and Electrolyte Balance
Water makes up over half of the human body, yet many women chronically under-consume this essential nutrient. Hydration impacts every physiological system—from cognitive function and skin elasticity to kidney filtration and metabolic rate. For womens daily wellbeing, consistent hydration is non-negotiable, particularly in hot climates, during intense workouts, or when consuming caffeine, which acts as a mild diuretic.
Plain water should be the foundation, but adding natural flavor from cucumber, citrus, or mint can make it more appealing. Herbal teas, coconut water, and bone broth also contribute to hydration while offering functional benefits like antioxidants or collagen. Women with high sweat loss from exercise or saunas should consider incorporating electrolytes—such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium—to prevent cramps, dizziness, and energy dips. These minerals help maintain fluid balance and support nerve and muscle function.
Signs of dehydration can be subtle, manifesting as headaches, fatigue, poor concentration, or sugar cravings. Monitoring urine color—pale yellow indicating adequate hydration—is a practical way to stay on track. Timing matters as well: starting the day with a glass of water reactivates the digestive system, while spacing intake throughout the day avoids overburdening the kidneys. Drinking too much water in short bursts can dilute sodium levels, so a steady pace is best.
For women prone to bloating or water retention, reducing processed foods and increasing potassium intake from bananas, sweet potatoes, and avocados can help. Hydration strategies should be adapted to menstrual phases too—during menstruation, blood loss may increase fluid needs, while during the luteal phase, rising progesterone may cause fluid shifts that impact hydration status. Being attuned to these rhythms can help women adjust water and electrolyte intake with precision.

Aging Gracefully: Nutritional Needs After Menopause
Menopause brings a wave of physiological change that alters nutrient requirements, metabolism, and hormonal balance. Declining estrogen levels affect bone density, cardiovascular health, and body composition, making it imperative to adopt a nutrition strategy that supports graceful aging without compromising vitality. Women in this life stage need tailored guidance to meet evolving dietary needs while maintaining energy, cognitive clarity, and independence.
Calcium, magnesium, vitamin D, and K2 take center stage for maintaining bone density and reducing the risk of osteoporosis. While dairy can be a good source of calcium, women with lactose intolerance or plant-based preferences should explore fortified plant milks, sesame seeds, and leafy greens. Including magnesium-rich foods like pumpkin seeds, legumes, and dark chocolate helps support both bone and cardiovascular function, while vitamin K2 ensures calcium is deposited in bones—not arteries.
Protein needs also increase with age to counteract sarcopenia, the gradual loss of muscle mass. Including 20–30 grams of protein per meal—sourced from lean meats, fish, legumes, or protein-rich smoothies—helps preserve lean body mass and metabolic health. Resistance training amplifies these benefits and supports posture, balance, and joint protection.
Heart health becomes increasingly important post-menopause, as estrogen’s protective effects wane. Emphasizing heart-friendly fats like olive oil, avocados, and flaxseeds while minimizing trans fats and excessive sodium can lower the risk of hypertension and stroke. Fiber also plays a key role in regulating cholesterol and supporting digestive health—goals that can be achieved through whole grains, legumes, and fruits like apples and berries.
Cognitive decline is another concern that can be mitigated through nutrition. Antioxidant-rich foods, B vitamins, and omega-3s continue to provide neuroprotection, while herbs like sage and turmeric may offer cognitive support. Women entering this new life chapter should see nutrition not as a list of restrictions but as a toolkit for longevity, clarity, and strength.
FAQ: Advanced Insights into Women’s Daily Wellness and Lifestyle Optimization
1. What are some lesser-known indicators that a women’s daily supplement is working effectively?
Beyond increased energy or improved skin health, subtle signs that a women’s daily supplement is working include enhanced cognitive clarity, more consistent bowel movements, and reduced frequency of minor illnesses like colds. You might also notice your sleep becoming more restorative, especially if the supplement contains magnesium or adaptogens. Over time, emotional stability and resilience to daily stressors can improve, reflecting enhanced hormonal balance and nervous system support. It’s important to track these changes across several menstrual cycles, as the benefits often unfold gradually. For best results, pair your womens daily supplement with regular check-ins on your physical and mental wellbeing.
2. How does a woman’s daily nutritional need shift during perimenopause and menopause?
During perimenopause and menopause, hormonal shifts dramatically alter the nutritional landscape. Women’s daily requirements for calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and omega-3s increase to help maintain bone density and reduce inflammation. B vitamins also become more critical for mood regulation and energy production as estrogen levels decline. A targeted womens daily supplement can ease symptoms such as hot flashes, brain fog, and irritability when formulated with phytoestrogens like black cohosh or red clover. These changes mean that women must reassess their supplement strategy regularly as they approach midlife. It’s also helpful to include micronutrients that support thyroid function, which may slow during this phase.
3. Why does consistency matter more than dosage in a woman’s daily wellness plan?
While proper dosing is essential, the consistency of intake plays a larger role in how the body absorbs and utilizes nutrients. Nutrient stores—especially for water-soluble vitamins like B-complex and vitamin C—deplete rapidly without regular replenishment. When a womens daily supplement is taken sporadically, the body struggles to maintain balance, which may lead to energy dips or weakened immune defense. Establishing a morning or evening ritual around your supplement intake increases adherence and can even psychologically reinforce healthy habits. This consistency supports long-term physiological adaptations, such as stabilized hormone cycles and improved metabolic efficiency.
4. Can a womens daily supplement support mental health alongside physical health?
Yes, many high-quality womens daily supplements now include ingredients that support brain chemistry and mood stabilization. Nutrients like zinc, vitamin D3, and magnesium play roles in neurotransmitter production, particularly serotonin and dopamine. In addition, adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha and rhodiola rosea help the body modulate cortisol and reduce stress-related fatigue. For women managing anxiety, PMS-related mood swings, or postnatal emotional changes, a carefully chosen supplement can be a powerful adjunct to therapy or lifestyle modifications. Mental health support through a woman’s daily nutritional intake represents a growing intersection of functional medicine and holistic self-care.
5. How does gut health influence the effectiveness of a woman’s daily supplement?
Your gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in nutrient absorption, immune regulation, and hormone metabolism. An imbalanced gut can impair the breakdown and uptake of essential vitamins and minerals, rendering even the best womens daily supplement less effective. Signs of poor gut health include bloating, irregular bowel movements, frequent illness, or chronic fatigue. Incorporating a daily probiotic or prebiotic fiber alongside your supplement routine enhances gut flora diversity and improves assimilation of nutrients. For optimal results, choose a supplement that includes digestive enzymes or is specifically labeled as “bioavailable” to enhance absorption.
6. How can a busy lifestyle impact the benefits of a woman’s daily wellness routine?
Fast-paced living often leads to nutrient depletion due to stress, poor diet, and irregular sleep. Even if you take a womens daily supplement, lifestyle stressors can interfere with nutrient utilization and overall wellness outcomes. For example, chronic stress raises cortisol, which can deplete B vitamins and magnesium—both essential for energy and mood regulation. To offset this, consider integrating mindfulness practices, hydration reminders, and nutrient-dense snacks into your daily routine. Viewing your supplement as part of a broader support system rather than a cure-all leads to more sustainable, long-term benefits.
7. What are the emerging trends in the womens daily supplement market?
The industry is evolving beyond one-size-fits-all multivitamins toward personalized and functional blends. Innovations include time-release capsules, hormone-specific formulations, and microbiome-targeted nutrients. Some women’s daily products now incorporate genomic data or lifestyle inputs to tailor micronutrient levels precisely. Clean-label supplements—free of synthetic dyes, allergens, or unnecessary binders—are becoming standard. Moreover, the rise of AI-powered nutrition apps allows women to track symptoms and adjust supplement routines dynamically, bridging the gap between conventional wellness and cutting-edge biohacking.
8. How can a woman’s daily supplement routine support long-term preventative health?
Incorporating a womens daily supplement into your routine is not just about immediate vitality—it can also offer long-term protective benefits. Key nutrients like folate, selenium, and antioxidants support DNA repair and cellular defense mechanisms, reducing the risk of chronic disease. Regular supplementation can also stabilize insulin response, cholesterol levels, and blood pressure over time, particularly when combined with a balanced diet. Preventative health also includes hormone health, and many daily formulas are now designed to modulate estrogen and progesterone naturally. Taking a proactive rather than reactive approach helps create a foundation of resilience as you age.
9. Why is the bioavailability of nutrients critical in a woman’s daily supplement?
Bioavailability refers to how well a nutrient is absorbed and used by the body, which can vary significantly depending on the supplement’s form. For example, magnesium glycinate is more bioavailable and gentler on the stomach than magnesium oxide. Similarly, methylated forms of B12 and folate are more effective for those with MTHFR gene variations. A high-quality womens daily supplement prioritizes forms that the body can use efficiently, often labeled as “chelated” or “activated.” Checking for clinical dosing and third-party testing ensures that you’re not just consuming nutrients—but actually benefiting from them.
10. How do social and cultural influences shape a woman’s daily health practices?
A woman’s daily wellness habits are often influenced by cultural expectations, social media trends, and community norms. In some societies, women prioritize external appearance over internal health due to beauty standards, which can overshadow essential self-care routines. Others may inherit dietary or lifestyle beliefs that impact supplement acceptance or selection. Social support—such as group fitness, wellness challenges, or family accountability—can encourage consistency with supplement use. Recognizing and reshaping these influences allows women to make health decisions rooted in empowerment and evidence, not just aesthetics or tradition.
Conclusion: Empowering Womens Daily Wellness Through Intentional Nutrition
True health is not defined by fleeting diets or the latest wellness trend, but by a foundation of consistent, nourishing choices that align with a woman’s evolving biological needs. By embracing essential nutrition tips tailored to support womens daily health goals, women can optimize hormonal balance, mental clarity, reproductive function, and long-term vitality across every life stage. Whether it’s prioritizing iron and B12 during reproductive years, incorporating omega-3s for anti-inflammatory support, or adjusting calcium and protein intake post-menopause, nutrition is the compass that guides women toward lifelong wellness.
The phrase “woman daily” doesn’t simply refer to a routine—it signifies a rhythm, a pattern of care that honors the body’s cues and cycles. It means starting each day with purpose, choosing foods that fuel both the mind and body, and cultivating resilience from the inside out. Health is not a destination but a relationship, and like any relationship, it thrives on attention, respect, and intention.
As scientific understanding of women’s nutritional needs deepens, it’s clear that a personalized, whole-foods-based approach offers the greatest potential for sustainable wellness. From hydration to micronutrient sufficiency and gut health to cognitive vitality, each choice adds up to a narrative of strength, clarity, and empowerment. Let every meal be a reaffirmation of this intention—a vote for energy, confidence, and well-being in the life of every woman, every single day.
Further Reading:
One A Day® Women’s Complete Multivitamin



